Evaluation of normal saline gel and ozone therapy effects on soft and hard tissue health in dental implant surgery
Evaluation of normal saline gel and ozone therapy effects on soft and hard tissue health in dental implant surgery
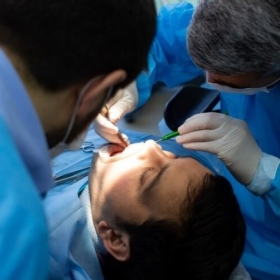
A recent study has shown that the use of ozone therapy while placing dental implants is effective in minimizing systemic inflammation, pain, and plaque deposition among dental implant recipients. The results of this study were published in the Indian Society for Dental Research.
Forty adult patients scheduled for implant placement were split into two groups: case group of twenty patients received ozone therapy, while the control group of twenty patients received normal saline and gel during the procedure. Inflammation and pain were monitored on the first- and the seventh-day, as well as at three- month intervals, by measuring C-reactive protein (CRP) levels and evaluating visual analogue scale (VAS) scores. At three months, soft tissue outcomes were assessed in terms of gingival index, plaque index, and pocket depth, while crestal bone loss was evaluated using radiographs.
Significantly higher mean CRP levels were observed in the control group in comparison to the case group on first and seventh day follow-ups (P value < 0.05). Additionally, mean VAS scores for pain were lower in the case group at all follow-ups, with statistical significance only on first day (P value = 0.061). The plaque index was significantly lower in the case group compared to the control group at the final follow-up (P value = 0.011). No significant difference was noted between the two groups in terms of crestal bone loss.
The above study demonstrated that the application of ozone therapy has proven to be successful in decreasing systemic inflammation, pain, and plaque deposition in patients who have undergone dental implant procedures.
Evaluation of normal saline gel and ozone therapy effects on soft and hard tissue health in dental implant surgery
Evaluation of normal saline gel and ozone therapy effects on soft and hard tissue health in dental implant surgery
A recent study has shown that the use of ozone therapy while placing dental implants is effective in minimizing systemic inflammation, pain, and plaque deposition among dental implant recipients. The results of this study were published in the Indian Society for Dental Research.
Forty adult patients scheduled for implant placement were split into two groups: case group of twenty patients received ozone therapy, while the control group of twenty patients received normal saline and gel during the procedure. Inflammation and pain were monitored on the first- and the seventh-day, as well as at three- month intervals, by measuring C-reactive protein (CRP) levels and evaluating visual analogue scale (VAS) scores. At three months, soft tissue outcomes were assessed in terms of gingival index, plaque index, and pocket depth, while crestal bone loss was evaluated using radiographs.
Significantly higher mean CRP levels were observed in the control group in comparison to the case group on first and seventh day follow-ups (P value < 0.05). Additionally, mean VAS scores for pain were lower in the case group at all follow-ups, with statistical significance only on first day (P value = 0.061). The plaque index was significantly lower in the case group compared to the control group at the final follow-up (P value = 0.011). No significant difference was noted between the two groups in terms of crestal bone loss.
The above study demonstrated that the application of ozone therapy has proven to be successful in decreasing systemic inflammation, pain, and plaque deposition in patients who have undergone dental implant procedures.









 Nephrology
Nephrology