Dentinal Hypersensitivity
Dentinal Hypersensitivity
Dentinal Hypersensitivity is a chronic condition with acute episodes. When dentine is exposed, which usually happens due to gingival recession & enamel damage (erosion, abrasion, attrition, and abfraction), external triggers (such as a cold drink) can stimulate the nerves inside the tooth, causing the characteristic short, sharp sensation of tooth sensitivity.1
The most common trigger for realizing sensitivity is cold.
1. Dababneh RH, Khouri AT, Addy M. Dentine hypersensitivity — an enigma? A review of terminology, mechanisms, aetiology and management. Br Dent J.1999;187:606–611.
 What is Calcium Sodium Phosphosilicate?
What is Calcium Sodium Phosphosilicate?
CSPS is a particulate, bioactive glass material that degrades in the aqueous oral environment to release calcium and phosphate ions, leading to formation of Hydroxycarbonate Apatite on the dentine surface. This process creates a physical barrier that mitigates the impact of external stimuli on fluid movement within dentinal tubules.1
1. S. Schlafer et al. Journal of Dentistry 91S (2019) 100003.
 Why Vantej?
Why Vantej?
- CSPS as the major ingredient
- Extra foaming & Mint flavor
- Extensively studied molecule
 Where to Use?
Where to Use?
In Dentinal Hypersensitivity
- Dentinal Hypersensitivity is a chronic condition with an acute episodes, usually stimulated by external triggers – mainly a cold beverage.1
- Drinking or eating something cold/freezing is the most common sensation to realize Dentinal Hypersensitivity.2,3
1. Dababneh RH, Khouri AT, Addy M. Dentine hypersensitivity — an enigma? A review of terminology, mechanisms, aetiology and management. Br Dent J.1999;187:60 –611.
2. Hydrodynamic Theory Kramer IRH. The relationship between dentine sensitivity and movements in the contents of dentinal tubules. Br Dent J. 1955;98:391–392.
3. Brännström M. The elicitation of pain in human dentine and pulp by chemical stimuli. Arch Oral Biol. 1962;7:59–62.
 How to Use?
How to Use?
- Squeeze some toothpaste about half the length of the bristle head and brush for 1-2 minutes using a gentle, vertical sweeping motion away from gums.
- Spit out the paste and rinse with water, do not swallow.
- Avoid eating or drinking anything within half an hour of brushing.
- Brush twice daily for best results.
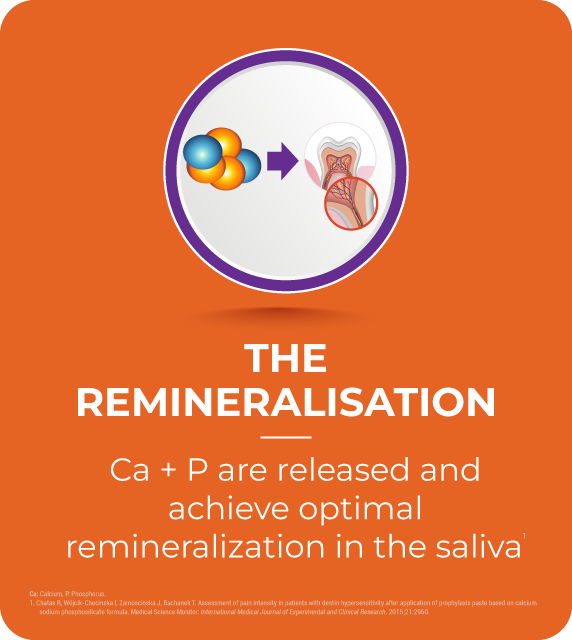
 Continued long-term release of Ca and P to build enamel layer
Continued long-term release of Ca and P to build enamel layer
- Vantej, when comes into contact with saliva, water releases particles of calcium and phosphorus ions, protected by the glass particles.
- Saliva gets saturated with the ions needed for remineralization.1
- Demineralized lesions attract Ca & P ions.1
- Building new hydroxy appetite crystals to remineralise the defect from roots to the top.
1. Anora B, et al. NovaMin and Dentin Hypersensitivity – In Vitro Evidence of Ecacy. J Clin Dent 2010.
Editor's Pick
FDI Criteria: A Standardized Approach to Evaluating Dental Restorations
FDI Criteria: A Standardized Approach to Evaluating Dental Restorations
World Dental Federation’s FDI Criteria: A New Standard for Evaluating Dental RestorationsFDI Criteria: A Standardized Approach to Evaluating Dental Restorations
The Crucial Role of Occlusion in Ensuring the Longevity of Dental Restorations
The Crucial Role of Occlusion in Ensuring the Longevity of Dental Restorations
The Crucial Role of Occlusion in Dental Restorations: Insights and Tools IntroductionThe Crucial Role of Occlusion in Ensuring the Longevity of Dental Restorations
Fish Bone-Derived Calcium Phosphate: A Sustainable Solution for Dental Remineralization and Sensitivity
Fish Bone-Derived Calcium Phosphate: A Sustainable Solution for Dental Remineralization and Sensitivity
From Ocean to Oral Health: Fish Bones Pave the Way for Dental InnovationsFish Bone-Derived Calcium Phosphate: A Sustainable Solution for Dental Remineralization and Sensitivity
Biomimetic Regenerative Dentistry: Harnessing Nature’s Blueprint for Advanced Tooth Repair
Biomimetic Regenerative Dentistry: Harnessing Nature’s Blueprint for Advanced Tooth Repair
Biomimetic Regenerative Dentistry: Unlocking Nature’s Blueprint for Perfect SmilesBiomimetic Regenerative Dentistry: Harnessing Nature’s Blueprint for Advanced Tooth Repair
Biomimetic Innovations: Transforming Restorative Dentistry for Better Tooth Preservation and Function
Biomimetic Innovations: Transforming Restorative Dentistry for Better Tooth Preservation and Function
How Biomimetic innovations are reshaping the restorative dentistryBiomimetic Innovations: Transforming Restorative Dentistry for Better Tooth Preservation and Function
Modern Mouth Rinses: A New Defense Against Erosive Tooth Wear
Modern Mouth Rinses: A New Defense Against Erosive Tooth Wear
A New Shield for Sensitive Teeth: How Modern Mouth Rinses Can Combat Erosive Tooth WearModern Mouth Rinses: A New Defense Against Erosive Tooth Wear
FDI Criteria: A Standardized Approach to Evaluating Dental Restorations
FDI Criteria: A Standardized Approach to Evaluating Dental Restorations
World Dental Federation’s FDI Criteria: A New Standard for Evaluating Dental RestorationsFDI Criteria: A Standardized Approach to Evaluating Dental Restorations
Impact of medications on dental health in Older adults
Impact of medications on dental health in Older adults
Polypharmacy and Its Impact on Older Patients Oral Health: What Every Dentist Needs to KnowImpact of medications on dental health in Older adults
Oral Health in Athletes
Oral Health in Athletes
Balancing Performance and Protection: How Sports Diets Affect Athlete’s Oral HealthOral Health in Athletes
Dipotassium oxalate and diode laser for dentinal hypersensitivity
Dipotassium oxalate and diode laser for dentinal hypersensitivity
Innovative Relief: Combining Lasers and Mouthwash for Sensitive TeethDipotassium oxalate and diode laser for dentinal hypersensitivity
Preemptive Ibuprofen and Potassium Fluoride Combination Reduces Tooth Sensitivity After Whitening
Preemptive Ibuprofen and Potassium Fluoride Combination Reduces Tooth Sensitivity After Whitening
A triple-blind, randomized clinical trial has shown that the preemptive use of ibuprofen (IBU) combined with potassium fluoride 2% (KF2) significantly reduces tooth sensitivity immediately after in-office bleaching procedures.
The study involved 15 participants using a crossover and split-mouth design to evaluate the analgesic effects of the combined treatment compared to ibuprofen or potassium fluoride alone and placebo. Participants reported tooth sensitivity levels on a visual analog scale at four intervals: immediately post-bleaching and at 6, 30, and 54 hours.
The combination of 400 mg of ibuprofen and 2% potassium fluoride outperformed the placebo group in reducing immediate tooth sensitivity (P < 0.05). Notably, the risk of experiencing moderate or severe sensitivity was four times higher in the placebo group compared to the combined treatment group (relative risk 4.00, 95% CI: 1.01–15.81, P = 0.025).
These findings suggest that the synergistic use of ibuprofen and potassium fluoride provides superior pain management during bleaching, making it a practical preemptive strategy for patients undergoing tooth whitening procedures. This approach can enhance patient comfort and satisfaction by minimizing post-bleaching sensitivity.
Preemptive Ibuprofen and Potassium Fluoride Combination Reduces Tooth Sensitivity After Whitening
Preemptive Ibuprofen and Potassium Fluoride Combination Reduces Tooth Sensitivity After Whitening
A triple-blind, randomized clinical trial has shown that the preemptive use of ibuprofen (IBU) combined with potassium fluoride 2% (KF2) significantly reduces tooth sensitivity immediately after in-office bleaching procedures.
The study involved 15 participants using a crossover and split-mouth design to evaluate the analgesic effects of the combined treatment compared to ibuprofen or potassium fluoride alone and placebo. Participants reported tooth sensitivity levels on a visual analog scale at four intervals: immediately post-bleaching and at 6, 30, and 54 hours.
The combination of 400 mg of ibuprofen and 2% potassium fluoride outperformed the placebo group in reducing immediate tooth sensitivity (P < 0.05). Notably, the risk of experiencing moderate or severe sensitivity was four times higher in the placebo group compared to the combined treatment group (relative risk 4.00, 95% CI: 1.01–15.81, P = 0.025).
These findings suggest that the synergistic use of ibuprofen and potassium fluoride provides superior pain management during bleaching, making it a practical preemptive strategy for patients undergoing tooth whitening procedures. This approach can enhance patient comfort and satisfaction by minimizing post-bleaching sensitivity.
Evaluation of post-operative pain in non-surgical root canal therapy: Comparison of sealer-based obturation with warm vertical compaction
Evaluation of post-operative pain in non-surgical root canal therapy: Comparison of sealer-based obturation with warm vertical compaction
Recent study results indicated that the sealer-based obturation (SBO) technique utilizing calcium silicate sealer (CSS) is correlated with similar post-operative pain levels and analgesic consumption as warm-vertical compaction (WVC) with resin-based sealer (RBS). Therefore, SBO with CSS may be a practical clinical alternative in the context of post-operative pain. The International Endodontic Journal has highlighted the results of this study.
This study included 195 patients who were referred for non-surgical root canal treatment (NSRCT) and fulfilled the essential inclusion criteria. Before the treatment, periapical radiographs and CBCT scans were conducted, and pain was assessed using a numerical rating scale (NRS). After completing the canal instrumentation, participants were randomly assigned to either Group SBO, which received SBO with CSS, or Group WVC, which utilized warm-vertical compaction with RBS. Post-operative pain levels and analgesic use were recorded at one, three, and seven days following the endodontic procedure. The differences in pain scores among the groups were assessed using the Mann-Whitney U and Friedman tests, while a generalized estimating equation was applied to evaluate correlations at different time points within each treatment group.
In the final analysis, 194 participants and 211 teeth were included, producing a response rate of 99.5%. There were no significant differences in post-operative pain or the use of analgesics between the two groups at any time point (p value > .05). On the other hand, pre-operative pain, age, apical diagnosis, and post-operative analgesic intake were significantly linked to post-operative pain (p value < .05).
The above findings indicated that the sealer-based obturation technique utilizing CSS is linked to post-operative pain and analgesic use that are comparable to warm-vertical compaction WVC with RBS. Therefore, SBO with CSS could be a practical alternative for managing pain after surgery.
Evaluation of post-operative pain in non-surgical root canal therapy: Comparison of sealer-based obturation with warm vertical compaction
Evaluation of post-operative pain in non-surgical root canal therapy: Comparison of sealer-based obturation with warm vertical compaction
Recent study results indicated that the sealer-based obturation (SBO) technique utilizing calcium silicate sealer (CSS) is correlated with similar post-operative pain levels and analgesic consumption as warm-vertical compaction (WVC) with resin-based sealer (RBS). Therefore, SBO with CSS may be a practical clinical alternative in the context of post-operative pain. The International Endodontic Journal has highlighted the results of this study.
This study included 195 patients who were referred for non-surgical root canal treatment (NSRCT) and fulfilled the essential inclusion criteria. Before the treatment, periapical radiographs and CBCT scans were conducted, and pain was assessed using a numerical rating scale (NRS). After completing the canal instrumentation, participants were randomly assigned to either Group SBO, which received SBO with CSS, or Group WVC, which utilized warm-vertical compaction with RBS. Post-operative pain levels and analgesic use were recorded at one, three, and seven days following the endodontic procedure. The differences in pain scores among the groups were assessed using the Mann-Whitney U and Friedman tests, while a generalized estimating equation was applied to evaluate correlations at different time points within each treatment group.
In the final analysis, 194 participants and 211 teeth were included, producing a response rate of 99.5%. There were no significant differences in post-operative pain or the use of analgesics between the two groups at any time point (p value > .05). On the other hand, pre-operative pain, age, apical diagnosis, and post-operative analgesic intake were significantly linked to post-operative pain (p value < .05).
The above findings indicated that the sealer-based obturation technique utilizing CSS is linked to post-operative pain and analgesic use that are comparable to warm-vertical compaction WVC with RBS. Therefore, SBO with CSS could be a practical alternative for managing pain after surgery.
Pain following endodontic procedures using 8.25% sodium hypochlorite vs. 2.5% sodium hypochlorite in necrotic mandibular molars with apical periodontitis
Pain following endodontic procedures using 8.25% sodium hypochlorite vs. 2.5% sodium hypochlorite in necrotic mandibular molars with apical periodontitis
According to a recent study, the application of 8.25% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) during endodontic treatment resulted in significantly more postoperative pain than 2.5% NaOCl, with pain scores increasing by 3.48 times. Additionally, pain was reported to be much more prevalent in the 8.25% NaOCl group than in the 2.5% NaOCl group during the period of twelve hours to three days. This study's outcomes were reported in the Journal of the American Dental Association.
A group of 154 patients was randomly assigned to two different concentrations of NaOCl: 8.25% and 2.5%. Postoperative pain was assessed at different intervals throughout a thirty day period using a numeric rating scale. The overall pain scores were examined over time using multilevel mixed-effects negative binomial regression. The need for pain relief medication was recorded and analyzed between the two groups using the Mann-Whitney U test.
The use of 8.25% NaOCl led to a significant elevation in postoperative pain scores, which were 3.48 times more than those seen with 2.5% NaOCl (incident rate ratio, 3.48; 95% confidence interval, 1.57 to 7.67). Additionally, the group treated with 8.25% NaOCl experienced greater pain incidence compared to the 2.5% NaOCl group during the twelve hours to three-day period, with pain scores ranging from 2.21 (IRR, 2.21; 95% confidence interval, 1.35 to 3.62) to 10.74 (IRR, 10.74; 95% confidence interval, 3.74 to 30.87) higher. The number of analgesic capsules used was similar across both groups.
The above study demonstrated that the use of 8.25% NaOCl increased the postoperative pain compared to 2.5% NaOCl. In addition, the incidence of pain was significantly higher in the 8.25% NaOCl group than in the 2.5% NaOCl group over the span of twelve hours to three days.
Pain following endodontic procedures using 8.25% sodium hypochlorite vs. 2.5% sodium hypochlorite in necrotic mandibular molars with apical periodontitis
Pain following endodontic procedures using 8.25% sodium hypochlorite vs. 2.5% sodium hypochlorite in necrotic mandibular molars with apical periodontitis
According to a recent study, the application of 8.25% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) during endodontic treatment resulted in significantly more postoperative pain than 2.5% NaOCl, with pain scores increasing by 3.48 times. Additionally, pain was reported to be much more prevalent in the 8.25% NaOCl group than in the 2.5% NaOCl group during the period of twelve hours to three days. This study's outcomes were reported in the Journal of the American Dental Association.
A group of 154 patients was randomly assigned to two different concentrations of NaOCl: 8.25% and 2.5%. Postoperative pain was assessed at different intervals throughout a thirty day period using a numeric rating scale. The overall pain scores were examined over time using multilevel mixed-effects negative binomial regression. The need for pain relief medication was recorded and analyzed between the two groups using the Mann-Whitney U test.
The use of 8.25% NaOCl led to a significant elevation in postoperative pain scores, which were 3.48 times more than those seen with 2.5% NaOCl (incident rate ratio, 3.48; 95% confidence interval, 1.57 to 7.67). Additionally, the group treated with 8.25% NaOCl experienced greater pain incidence compared to the 2.5% NaOCl group during the twelve hours to three-day period, with pain scores ranging from 2.21 (IRR, 2.21; 95% confidence interval, 1.35 to 3.62) to 10.74 (IRR, 10.74; 95% confidence interval, 3.74 to 30.87) higher. The number of analgesic capsules used was similar across both groups.
The above study demonstrated that the use of 8.25% NaOCl increased the postoperative pain compared to 2.5% NaOCl. In addition, the incidence of pain was significantly higher in the 8.25% NaOCl group than in the 2.5% NaOCl group over the span of twelve hours to three days.
Ozone Therapy Demonstrates Superior Long-Term Relief for Dentin Hypersensitivity
Ozone Therapy Demonstrates Superior Long-Term Relief for Dentin Hypersensitivity
A recent randomized clinical study has revealed that ozone gas treatment provides more sustained relief from dentin hypersensitivity (DHS) than diode laser therapy.
The study involved 44 patients with moderate DHS, encompassing 132 teeth, which were randomized into three groups using a split-mouth design:
- ozone gas treatment
- diode laser treatment
- placebo group receiving no therapy
In the ozone gas group, a high dose of ozone (32 g/m³) was applied for 30 seconds using a silicone cup. The diode laser group received irradiation of the exposed dentin with an 808-nm wavelength laser at incremental power levels ranging from 0.2 to 0.6 W, with 20-second intervals.
Dentin sensitivity was assessed at baseline, immediately after treatment, and at 3 and 6 months post-treatment using cold air blast and tactile stimuli. Pain severity was quantified using a visual analogue scale.
Both ozone gas and diode laser treatments resulted in a significant immediate decrease in DHS compared to the placebo group. However, after six months, the teeth treated with ozone gas maintained significantly lower sensitivity levels than those treated with diode lasers (P < .05). This indicates that while both treatments are effective initially, ozone therapy offers more enduring benefits for DHS management.
The findings suggest that ozone gas treatment may be a more advantageous option for long-term relief of dentin hypersensitivity, potentially improving patient comfort and reducing the need for repeated interventions over time.
Ozone Therapy Demonstrates Superior Long-Term Relief for Dentin Hypersensitivity
Ozone Therapy Demonstrates Superior Long-Term Relief for Dentin Hypersensitivity
A recent randomized clinical study has revealed that ozone gas treatment provides more sustained relief from dentin hypersensitivity (DHS) than diode laser therapy.
The study involved 44 patients with moderate DHS, encompassing 132 teeth, which were randomized into three groups using a split-mouth design:
- ozone gas treatment
- diode laser treatment
- placebo group receiving no therapy
In the ozone gas group, a high dose of ozone (32 g/m³) was applied for 30 seconds using a silicone cup. The diode laser group received irradiation of the exposed dentin with an 808-nm wavelength laser at incremental power levels ranging from 0.2 to 0.6 W, with 20-second intervals.
Dentin sensitivity was assessed at baseline, immediately after treatment, and at 3 and 6 months post-treatment using cold air blast and tactile stimuli. Pain severity was quantified using a visual analogue scale.
Both ozone gas and diode laser treatments resulted in a significant immediate decrease in DHS compared to the placebo group. However, after six months, the teeth treated with ozone gas maintained significantly lower sensitivity levels than those treated with diode lasers (P < .05). This indicates that while both treatments are effective initially, ozone therapy offers more enduring benefits for DHS management.
The findings suggest that ozone gas treatment may be a more advantageous option for long-term relief of dentin hypersensitivity, potentially improving patient comfort and reducing the need for repeated interventions over time.
Pain following endodontic procedures using 8.25% sodium hypochlorite vs. 2.5% sodium hypochlorite in necrotic mandibular molars with apical periodontitis
Pain following endodontic procedures using 8.25% sodium hypochlorite vs. 2.5% sodium hypochlorite in necrotic mandibular molars with apical periodontitis
According to a recent study, the application of 8.25% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) during endodontic treatment resulted in significantly more postoperative pain than 2.5% NaOCl, with pain scores increasing by 3.48 times. Additionally, pain was reported to be much more prevalent in the 8.25% NaOCl group than in the 2.5% NaOCl group during the period of twelve hours to three days. This study's outcomes were reported in the Journal of the American Dental Association.
A group of 154 patients was randomly assigned to two different concentrations of NaOCl: 8.25% and 2.5%. Postoperative pain was assessed at different intervals throughout a thirty day period using a numeric rating scale. The overall pain scores were examined over time using multilevel mixed-effects negative binomial regression. The need for pain relief medication was recorded and analyzed between the two groups using the Mann-Whitney U test.
The use of 8.25% NaOCl led to a significant elevation in postoperative pain scores, which were 3.48 times more than those seen with 2.5% NaOCl (incident rate ratio, 3.48; 95% confidence interval, 1.57 to 7.67). Additionally, the group treated with 8.25% NaOCl experienced greater pain incidence compared to the 2.5% NaOCl group during the twelve hours to three-day period, with pain scores ranging from 2.21 (IRR, 2.21; 95% confidence interval, 1.35 to 3.62) to 10.74 (IRR, 10.74; 95% confidence interval, 3.74 to 30.87) higher. The number of analgesic capsules used was similar across both groups.
The above study demonstrated that the use of 8.25% NaOCl increased the postoperative pain compared to 2.5% NaOCl. In addition, the incidence of pain was significantly higher in the 8.25% NaOCl group than in the 2.5% NaOCl group over the span of twelve hours to three days.
Pain following endodontic procedures using 8.25% sodium hypochlorite vs. 2.5% sodium hypochlorite in necrotic mandibular molars with apical periodontitis
Pain following endodontic procedures using 8.25% sodium hypochlorite vs. 2.5% sodium hypochlorite in necrotic mandibular molars with apical periodontitis
According to a recent study, the application of 8.25% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) during endodontic treatment resulted in significantly more postoperative pain than 2.5% NaOCl, with pain scores increasing by 3.48 times. Additionally, pain was reported to be much more prevalent in the 8.25% NaOCl group than in the 2.5% NaOCl group during the period of twelve hours to three days. This study's outcomes were reported in the Journal of the American Dental Association.
A group of 154 patients was randomly assigned to two different concentrations of NaOCl: 8.25% and 2.5%. Postoperative pain was assessed at different intervals throughout a thirty day period using a numeric rating scale. The overall pain scores were examined over time using multilevel mixed-effects negative binomial regression. The need for pain relief medication was recorded and analyzed between the two groups using the Mann-Whitney U test.
The use of 8.25% NaOCl led to a significant elevation in postoperative pain scores, which were 3.48 times more than those seen with 2.5% NaOCl (incident rate ratio, 3.48; 95% confidence interval, 1.57 to 7.67). Additionally, the group treated with 8.25% NaOCl experienced greater pain incidence compared to the 2.5% NaOCl group during the twelve hours to three-day period, with pain scores ranging from 2.21 (IRR, 2.21; 95% confidence interval, 1.35 to 3.62) to 10.74 (IRR, 10.74; 95% confidence interval, 3.74 to 30.87) higher. The number of analgesic capsules used was similar across both groups.
The above study demonstrated that the use of 8.25% NaOCl increased the postoperative pain compared to 2.5% NaOCl. In addition, the incidence of pain was significantly higher in the 8.25% NaOCl group than in the 2.5% NaOCl group over the span of twelve hours to three days.
How would you rate this Medshorts
Thank you !
Your rating has been recorded.
Videos Speakers
Videos Speakers
Want our representative to contact you ?
Below fields are needed for webinar purpose.