 Where to use?
Where to use?
CIDMUS is indicated to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure in adult patients with chronic heart failure with a reduced ejection fraction
Knowledge Hub
CIDMUS Range

Storage: Store in a cool place
Shelf Life: 36 months from the date of manufacture
Precaution: Keep out of reach of children
Packs:
50 mg: Pack of 28 tablets (blister strip of 2 x 14)
100 mg: Pack of 28 tablets (blister strip of 2 x 14)
200 mg: Pack of 28 tablets (blister strip of 4 x 7)
Before prescribing, please consult full prescribing information available from India BSS dtd 28th Aug 17 based on international BSS dtd 10th Jul 17 effective from 18th Jan 2018
Indications: To reduce the risk of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure in patients with chronic heart failure (NYHA Class II-IV) and reduced ejection fraction. Dosage & Administration: Adults: The target dose of CIDMUS is 200 mg twice daily. The recommended starting dose of CIDMUS is 100 mg twice daily. A starting dose of 50 mg twice daily is recommended for patients not currently taking an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor or an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB), and should be considered for patients previously taking low doses of these agents. Double the dose every 2-4 weeks to the target of 200 mg twice daily, as tolerated by the patient. Geriatric patients: No dosage adjustment is required. Pediatric patients: CIDMUS has not been studied. Use of CIDMUS is not recommended. Renal impairment: No dose adjustment is required in patients with mild to moderate renal impairment; A starting dose of 50 mg twice daily and caution is recommended in patients with severe renal impairment. Hepatic impairment: No dose adjustment is required in patients with mild hepatic impairment. A starting dose of 50 mg twice daily is recommended in patients with moderate hepatic impairment. In patients with severe hepatic impairment use of CIDMUS is not recommended. Method of administration: For oral use. May be administered with or without food. Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to the active substance, sacubitril, valsartan, or to any of the excipients. Concomitant use with ACE inhibitors. CIDMUS must not be administered until 36 hours after discontinuing ACE inhibitor therapy. Known history of angioedema related to previous ACE inhibitor or ARB therapy. Hereditary angioedema. Concomitant use with aliskiren in patients with Type 2 diabetes. Pregnancy. Warnings and precautions: Dual blockade of the Renin-Angiotensin- Aldosterone System (RAAS): CIDMUS must not be administered with an ACE inhibitor due to the risk of angioedema. CIDMUS must not be initiated until 36 hours after taking the last dose of ACE inhibitor therapy. If treatment with CIDMUS is stopped, ACE inhibitor therapy must not be initiated until 36 hours after the last dose of CIDMUS. CIDMUS must not be administered with aliskiren in patients with Type 2 diabetes. CIDMUS should not be co-administered with an ARB due to the angiotensin II receptor blocking activity of CIDMUS. Concomitant use with aliskiren should be avoided in patients with renal impairment (eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2)
Hypotension: If hypotension occurs, dose adjustment of diuretics, concomitant antihypertensive drugs, and treatment of other causes of hypotension (e.g. hypovolemia) should be considered. If hypotension persists despite such measures, the dosage of CIDMUS should be reduced or the product should be temporarily discontinued. Permanent discontinuation of therapy is usually not required. Sodium and/or volume depletion should be corrected before starting treatment with CIDMUS.
Impaired renal function: Down titration of CIDMUS should be considered in patients who develop a clinically significant decrease in renal function. Caution should be exercised when administering CIDMUS in patients with severe renal impairment.
Hyperkalemia: Medications known to raise potassium levels (e.g. potassium-sparing diuretics, potassium supplements) should be used with caution. If clinically significant hyperkalemia occurs, measures such as reducing dietary potassium, or adjusting the dose of concomitant medications should be considered Monitoring of serum potassium is recommended especially in patients with risk factors such as severe renal impairment, diabetes mellitus, hypoaldosteronism or receiving a high potassium diet.
Angioedema: If angioedema occurs, CIDMUS should be immediately discontinued and appropriate therapy and monitoring should be provided until complete and sustained resolution of signs and symptoms has occurred. CIDMUS must not be re-administered. Patients with a prior history of angioedema were not studied. As they may be at higher risk for angioedema, caution is recommended if CIDMUS is used in these patients. CIDMUS must not be used in patients with a known history of angioedema related to previous ACE inhibitor or ARB therapy, or in patients with hereditary angioedema. Black patients may have increased susceptibility to develop angioedema.
Patients with renal artery stenosis: Caution is required in patients with renal artery stenosis and monitoring of the renal function is recommended.
Pregnancy: CIDMUS must not be used during pregnancy. Patients should be advised to discontinue CIDMUS as soon as pregnancies occur and to inform their physicians. Females of child-bearing potential: Female patients of childbearing potential should be advised about the consequences of exposure to CIDMUS during pregnancy and to use contraception during treatment and for 1 week after their last dose of CIDMUS. Breast-feeding: It is not known whether CIDMUS is excreted in human milk. Because of the potential risk for adverse drug reactions in breastfed newborns/infants, CIDMUS is not recommended during breastfeeding. Adverse drug reactions: Very common (≥10%): Hyperkalemia, hypotension, renal impairment. Common (1 to 9%): Cough, Dizziness, renal failure, diarrhea, hypokalemia, fatigue, headache, syncope, nausea, asthenia, orthostatic hypotension, vertigo. Uncommon (0.1 to 1%): Angioedemia, dizziness postural. Unknown: Hypersensitivity (including rash, pruritus, and anaphylaxis).
Interactions: Concomitant use contraindicated: aliskiren in patients with Type 2 diabetes, Use with ACE inhibitors. CIDMUS must not be started until 36 hours after taking the last dose of ACE inhibitor therapy. ACE inhibitor therapy must not be started until 36 hours after the last dose of CIDMUS.
Concomitant use not recommended: ARB, concomitant use of CIDMUS with aliskiren, should be avoided in patients with renal impairment (eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 ). Caution when used concomitantly with statins, sildenafil, lithium, potassium-sparing diuretics including mineral corticoid antagonists (e.g. spironolactone, triamterene, amiloride), potassium supplements, or salt substitutes containing potassium, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents (NSAIDs) including selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors (COX-2 Inhibitors), inhibitors of OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OAT3 (e.g. rifampin, cyclosporine) or MPR2 (e.g. ritonavir).
GGI-CO-A1-AQS-300037995-AM-G23-0173








 How to use?
How to use?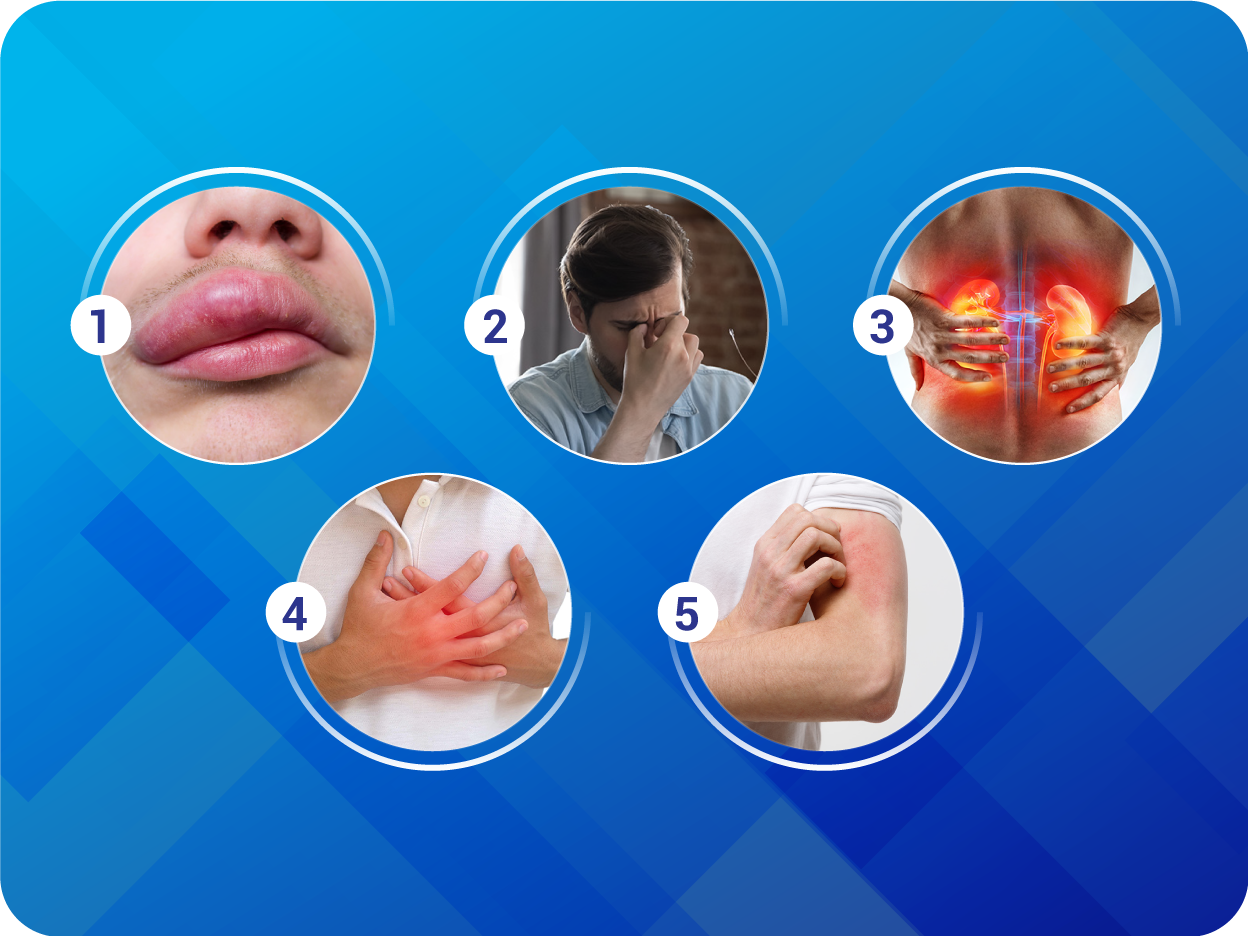 What are the Side Effects?
What are the Side Effects?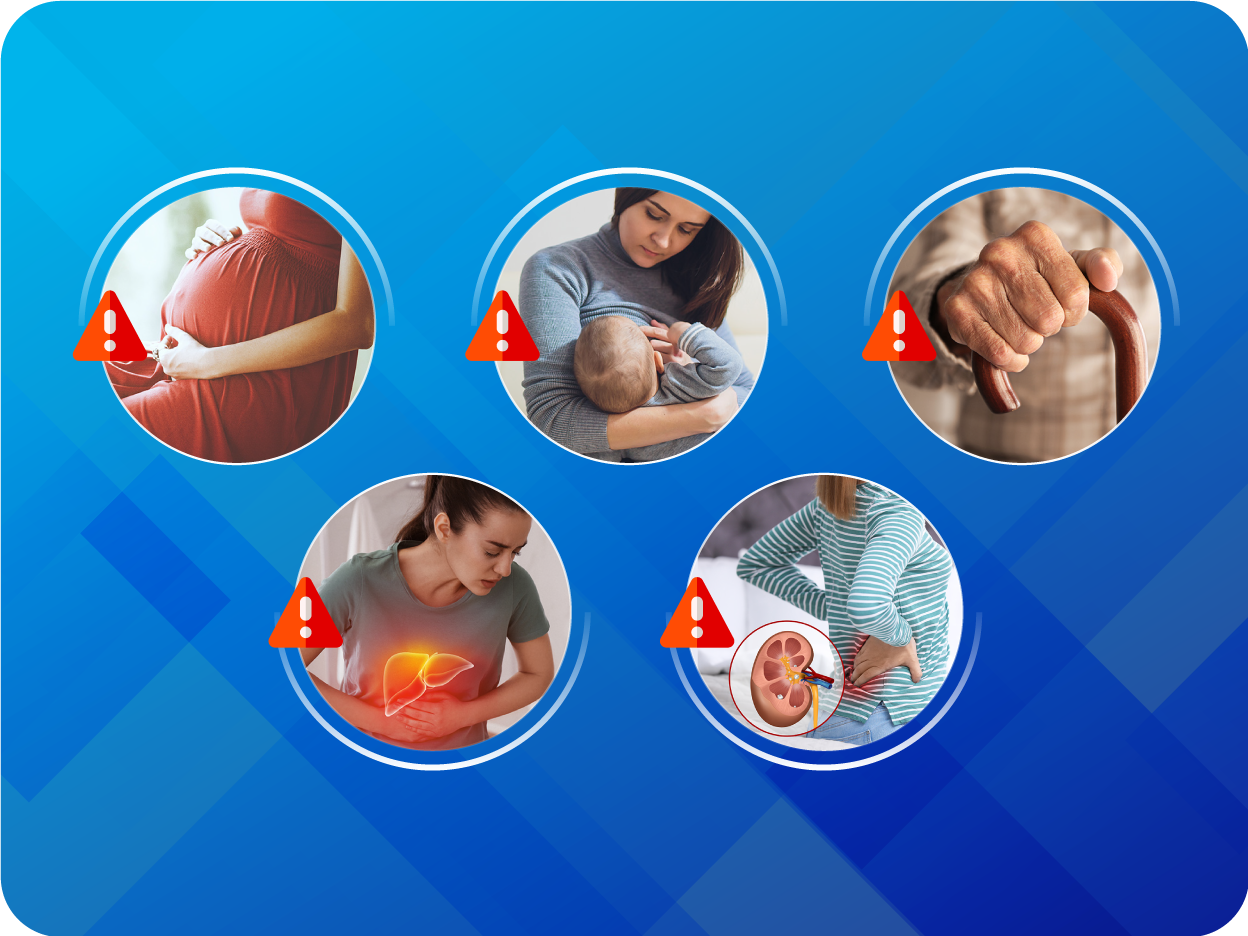 Safety Advice
Safety Advice Drug Interaction
Drug Interaction