
Atarax: Ease out discomfort and embarrassment to Pruritus in your patients
Where to use?

How to use?
Atarax 10 or 25-mg hydroxyzine hydrochloride tablets can be taken with or without food.
Adults: For symptomatic treatment of Pruritus:
Start with a dose of 10 or 25-mg of Atarax at night right before going to bed, preceded by additional 3-4 similar doses every day.
Children (above 12 months old): For symptomatic treatment of Pruritus:
For children above the age of 12 months, 1-mg/kg per day up to 2.5-mg/kg per day in divided doses is safe.

What are the side effects of Hydroxyzine Antihistamine?

Please refer to the prescribing information for the complete list of side effects.
Consult your doctor in case the side effects persist.
Safety Advices for Hydroxyzine Hydrochloride

Patients with a history of hypersensitivity to any of the constituents of Atarax, Cetirizine, or any other Piperazine derivatives, Aminophylline, and Ethylenediamine need to be careful with the intake of Atarax.

Patients suffering from Porphyria and with pre-existing prolonged QT interval should also take this medication with caution.

Caution is advised if the patient is pregnant or planning to conceive during the treatment and/or breast feeding.

Atarax should be administered cautiously in patients with increased potential for convulsions.
-
-
Derma
-
-
Videos Speakers
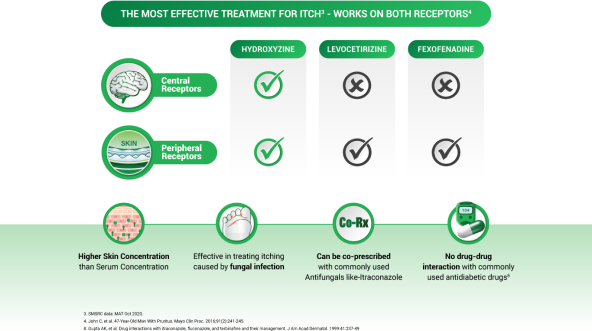
Why Hydroxyzine?
Hydroxyzine is used to treat itching caused by allergies. It is an Antihistamine and works by blocking a certain natural substance (Histamine) that body makes during allergic reactions during some conditions like dermatitis, Eczema, and Chronic Utricaria. Hydroxyzine may als be used short-term to treat Anxiety as it reduces the activity in the Central Nervous System, and it also helps you feel sleepy/relaxed before and after surgery.
-
Hydroxyzine: An Effective Antihistamine and the Drug of Choice for Pruritus
Read More -
Fever with skin rashes one of the first presentation of COVID-19
-

Study: Itch in children v/s itch in adults
-
Review: Emerging fungal infections in children and their iclinical manifestations, diagnosis, and prevention
-

Guidelines: How to avoid Misdiagnosis and Mistreatment of Atopic Dermatitis
-
First-generation antihistamines improves pruritus
-
Diabetes can cause local Itching
-
Common skin itching during monsoon
-

Pramoxine Hydrochloride improves Uremic Pruritis: Review Article
-
Underlying cause identification of chronic itch: Recent Research
-

Uremic Pruritus in Hemodialysis Patient: Trial Report
-
Uremic Pruritus: Therapies & their efficacy
-
Uremic Pruritus in patients with CKD
-

Promaxine-based Anti-itch Lotion v/s Control Lotion
-

Atopic Dermatitis: Clinically Meaningful Changes
-

Treatment Guidelines: Optimal Care of the Pediatric Patient with Psoriasis
-
Novel Systemic Therapies reveal promising results in care for patients with Atopic Dermatitis
-
Neonatal rash due to Pemphigoid Gestationis
-
Study: Multidisciplinary approach yields better outcome in treatment of Pediatric Atopic Dermatitis
-
Pediatric Atopic Dermatitis: New developments in therapies for transformation of management
-
Study Report: How to manage Annular Lesions in Pediatric Population
-

Case Study: Giant Urticaria and Acral Peeling in a Child with COVID‐19 associated manifestations
-

H1-Antihistamines and itch in Atopic Dermatitis
-

Itch Management for Diabetics
-

Atarax Anti-itch Lotion – Symptomatic & Soothing Relief from Itch
-
Itch in children
-

Atarax: The most effective treatment for itch
-
Study: Management of Scabies with Ivermectin-based MDA
-
Review highlights: A stepwise Pharmacological approach to treat Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria
-
Atopic Dermatitis is a risk factor for Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
-
Study: New drug advancement for AD set to reduce its Global burden
-
Study: Treating Vulvar Pruritus Multimodal Strategy with an Interdisciplinary Approach
-
Summary by Italian Expert Group: Pruritus in children with AD
-
British Association of Dermatologists: Hydroxyzine improves GPUO in adults
-
Report: Efficacy of Hydroxyzine to manage Uremic Pruritus in Hemodialysis patients
-

Recent Developments: Latest Approach to identify Cause and Management of Chronic Itch
-

Beneficial Effects of H-1 Antihistamine in Dermatological practices other than Itch and Urticaria Control
-

Guidelines: Treating Atopic Dermatitis (Consensus-based)
-
Novel Systemic Therapies for patients with Atopic Dermatitis
-
Study: Molecular pathways of Psoriatic Itch
Below fields are needed for webinar purpose.








