High Dose, Zero Hassle: Achieve Effortless Disimpaction With PEG, Muout, Paediatrician, Pediatrics, Pediatric Functional Constipation, High Dose, Zero Hassle, Effortless Disimpaction, PEG

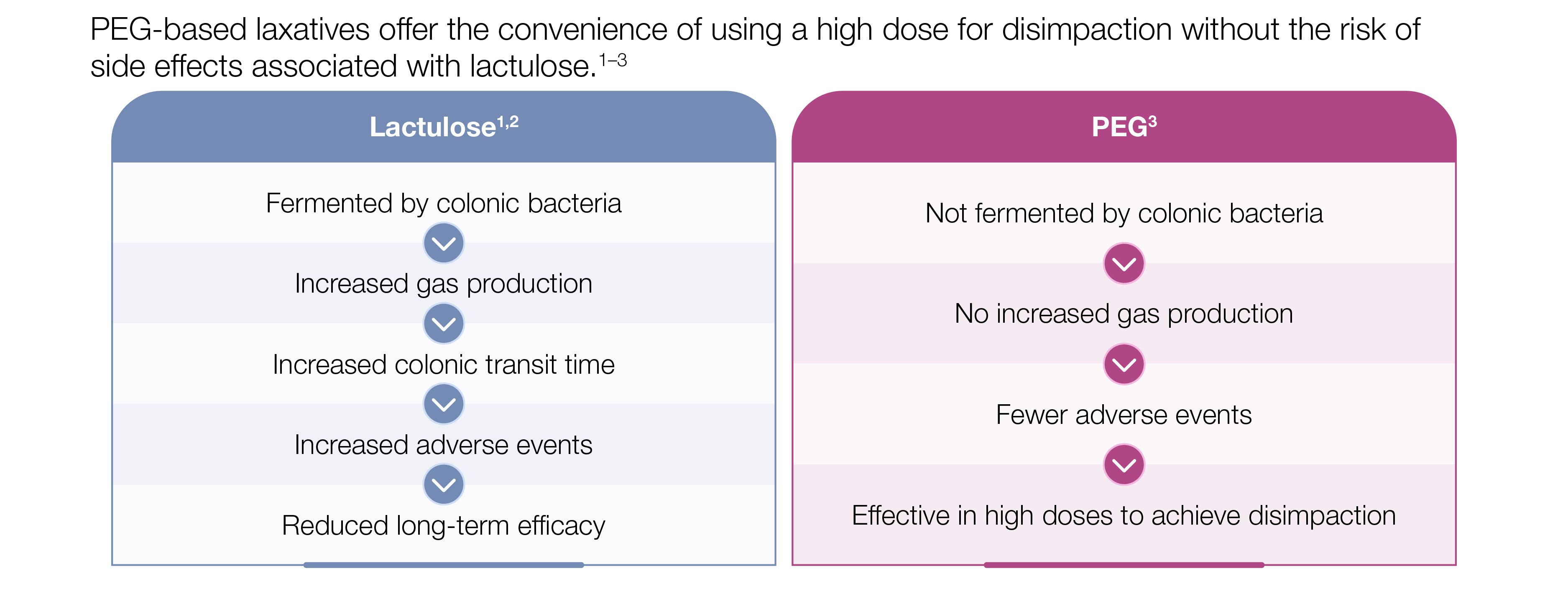
Embrace Early Fecal Disimpaction With PEG for Pediatric Well-being
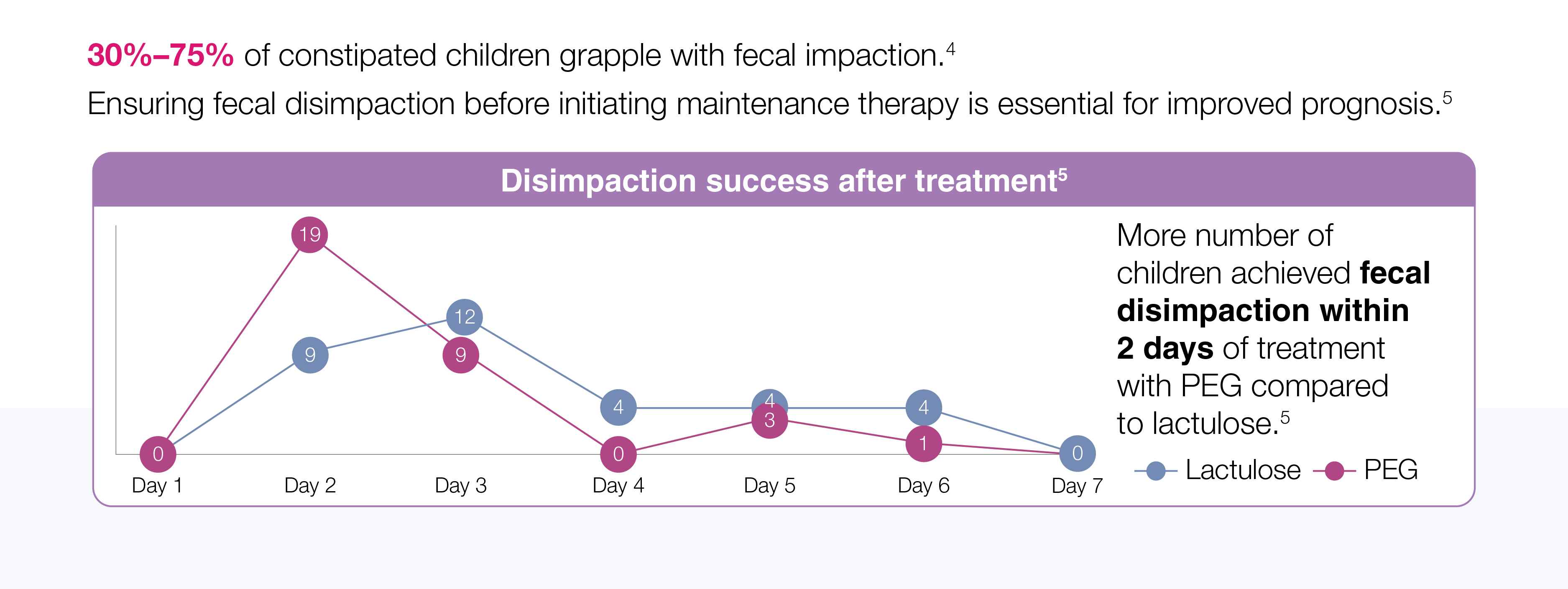
Ensure Uninterrupted Relief for Lasting Comfort in Kids

Transform Pediatric Functional Constipation Care With PEG: The Most Preferred Laxative

# IAP Guidelines 2018 and ESPGHAN and NASPGHAN Guidelines 2014. ^IAP recommends osmotic laxatives.$ In children >1 year. Each scoop contains 9.5 g of PEG. *Data on file.
The minimum recommended dosage as per IAP/NASPGHAN guidelines and approximation of dosage is rounded off to nearest 0.5 decimal.
Abbreviations
ESPGHAN: European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition; FC: Functional constipation; FU: Follow-up; IAP: Indian Academy of Pediatrics; NASPGHAN: North American Society For Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition; PEG: Polyethylene glycol; QoL: Quality of life.
References
1. Thompson AP, Wine E, MacDonald SE, et al. Parents’ experiences and information needs while caring for a child with functional constipation: A systematic review. Clin Pediat. 2021;60(3):154–169. 2. Loening-Baucke V, Krishna R, Pashankar DS. Polyethylene glycol 3350 without electrolytes for the treatment of functional constipation in infants and toddlers. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2004;39(5):536–539. 3. Loening-Baucke V, Pashankar DS. A randomized, prospective, comparison study of polyethylene glycol 3350 without electrolytes and milk of magnesia for children with constipation and fecal incontinence. Pediatrics. 2006;118(2):528–535. 4. Yachha SK, Srivastava A, Mohan N, et al. Indian Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Committee on childhood functional constipation, and Pediatric Gastroenterology Subspecialty Chapter of Indian Academy of Functional Constipation, and Pediatric Gastroenterology Subspecialty Chapter of Indian Academy of Pediatrics. Management of Childhood Functional Constipation: Consensus Practice Guidelines of Indian Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology. Indian Pediatr. 2018;55(10):885–892. 5. Pashankar DS, Bishop WP. Efficacy and optimal dosing of daily polyethylene glycol 3350 for treatment of constipation and encopresis in children. J Pediatr. 2001;139(3):428–432. 6. Chung S, Cheng A, Goldman RD. Polyethylene glycol 3350 without electrolytes for treatment of childhood constipation. Can Fam Physician. 2009;55(5):481–482. 7. Tabbers MM, DILorenzo C, Berger MY, et al. European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition: North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology. Evaluation and treatment of functional constipation in infants and children: Evidence-based recommendations from ESPGHAN and NASPGHAN. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2014;58(2):258–274.
LMRC Code: GGI-CO-A1-AQS-DCVP-BANNERS-A24-0203



















